Grove 125KHz RFID Reader
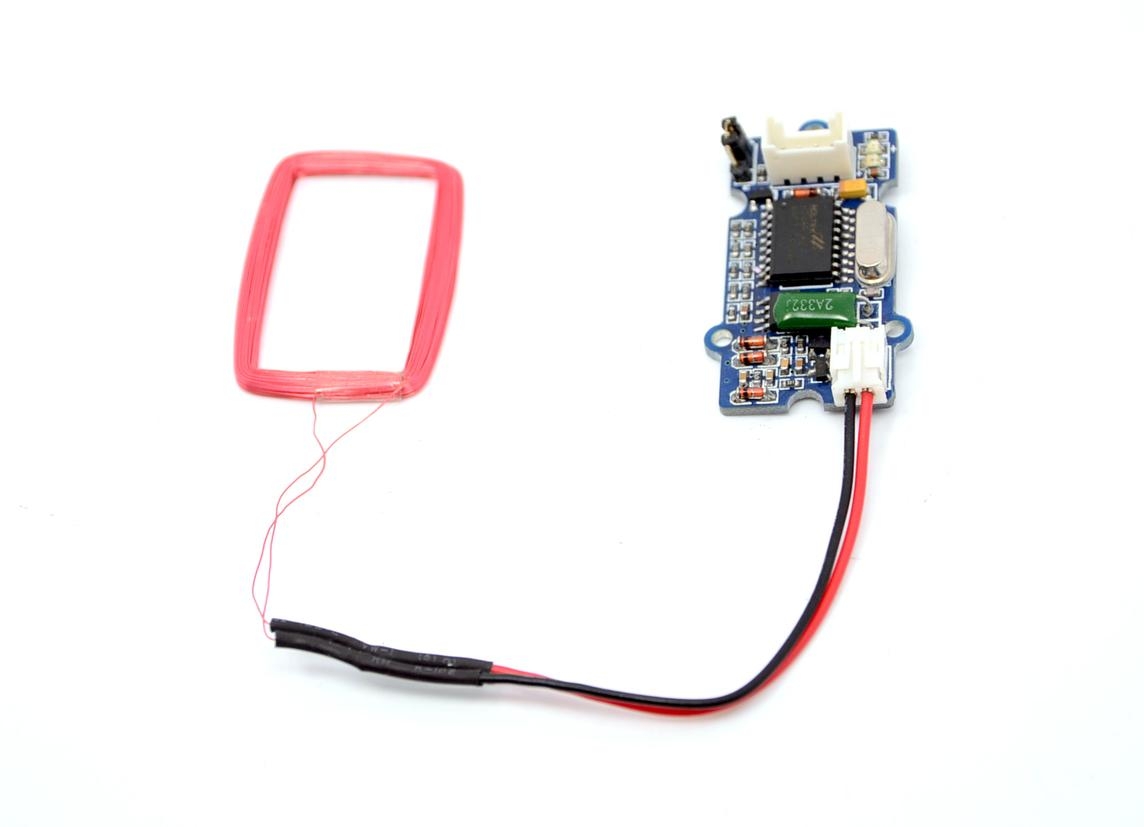

This Grove-125KHz RFID Reader is a module used to read uem4100 RFID card information with two output formats: Uart and Wiegand. It has a sensitivity with maximum 7cm sensing distance. There is also the electronic brick version of this module. It can help you with project like internet of thing and access control system.
And you should use the module below while using RFID reader:
Specifications
Voltage: 4.75-5.25V
Working Frequency: 125 KHz
Sensing Distance(Max): 70mm
TTL Output: 9600 baudrate, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no verify bit
Wiegand Output: 26 bits Wiegand format, 1 even verify bit, 24 data bits, and 1 odd verify bit
!!!Tip More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Platforms Supported
Demonstration
Here we show how to read RFID information using the Grove - 125KHz RFID Reader. Connect Grove - 125KHz RFID Reader to UART of Grove - Base Shield.
Uart Mode (Jumper set to the left two pins)
You would need to select the jumper to "U" to enter this mode, and the setting is: 9600bps, N, 8, 1, TTL output
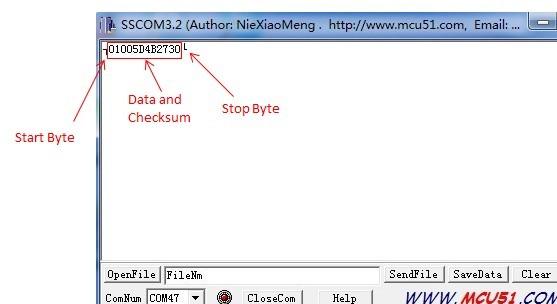
Open the Serial Monitor, the card information can be displayed as shown below:
Wiegand Mode (Jumper Set to the Right two Pins)
You would need to select the jumper to "W" to enter this mode. The Wiegand demo code for Seeeduino is designed to read Wiegand data in interrupt mode.
In Wiegand Mode, output data is formatted with 26bits including 24bits card info and 2 bits parity.
bit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
-
PE
D
P0
-
-
E
0
-
-
-
D2[7..0]
D1[7..0]
D0[7..0]
-
PE is even bit, PO is odd bit;
E is the data bit which was involved in even, O is the data bit which was involved in odd;
DX[7..0] is the data bit which correspond to Mifare@ Standard & Light card read only ID;
How to convert the output to Card Number
Take ID: 0009776930 for example:
Card Number ID: 0009776930 ------- Decimalism [Start Bit(00) + Card Number(8 numbers)]
Output: 0700952F229F ------------- Hex [[Start Bit(07h) + Card Number(8 numbers) + Checksum]
The calculator for decimal and hex numbers is available online.
Last updated