Grove UART Wifi

Grove - UART WiFi is a serial transceiver module featuring the ubiquitous ESP8266 IoT SoC. With integrated TCP/IP protocol stack, this module lets your micro-controller interact with WiFi networks with only a few lines of code. Each ESP8266 module comes pre-programmed with an AT command set firmware, meaning you can send simple text commands to control the device. The SoC features integrated WEP, WPA/WPA2, TKIP, AES, and WAPI engines, can act as an access point with DHCP, can join existing WiFi networks and has configurable MAC and IP addresses.
Features
Grove 4-pin connector (RX,TX,VCC,GND)
802.11 b/g/n protocol (2.4GHz)
WiFi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
Supports three modes: AP, STA and AP+STA coexistence mode
Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
LwIP (lightweight IP)
Integrated low power 32-bit CPU could be reprogrammed as an application processor
Integrated temperature sensor
Serial UART Interface
Multi-queue QoS management
Wake up and transmit packets in < 2ms
Metal shielding
On-board ceramic antenna
Reset switch
!!!Tip More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Hardware Overview
Here is block diagram of Grove - UART WiF module which consists of following parts.
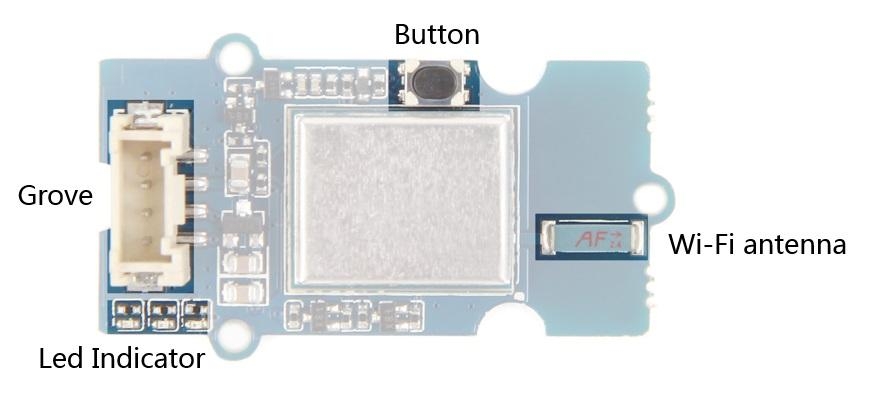
Grove - Used to connect to a processor through socket on a base board such as a Seeeduino or Grove Base Shield.
WiFi antenna - Antenna for ESP8266(Module model)
Button - With multi-functions
Reset - Press down and release quickly.
Set ESP8266(Module model) into UART boot mode - Press and hold button until centred red LED indicator light on.
Led Indicator - Used to indicate working status and for operations by user.
Left - a blue LED indicator - Controlled by user through command "AT+LEDON" and "AT+LEDOFF".
Middle - a red LED indicator - light on while Wifi connected or go into UART boot mode
Right - a green LED indicator - light on while power on.
Specifications
Input voltage: 3V / 5V
Baud Rate: 115200
Based on ESP8266 ESP-06 SoC
AT Firmware: esp_iot_sdk_v1.1.0 + Seeed modifications:
2x additional AT commands to control blue Link LED.
Register red WiFi LED to the ESP8266 wifi state LED.
AT command set
SDIO 1.1/2.0, SPI, UART
Five power states: OFF, DEEP_SLEEP, SLEEP, WAKEUP and ON.
Standby power consumption of < 1.0mW (DTIM=3)
Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
Integrated PLLs, regulators, DCXO and power management units
+19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
Power down leakage current of <10uA
Hardware accelerators for CCMP (CBC-MAC, counter mode), TKIP (MIC, RC4), WAPI (SMS4), WEP (RC4), CRC
WPA/WPA2 PSK, and WPS driver
A-MPDU & A-MSDU aggregation & 0.4ms guard interval
Dimensions: 25.43mm x 20.35mm
Ultra-low power technology
The ESP8266 was designed to achieve very low energy consumption with patented power management technology that reduces non-essential functions and regulates sleep patterns. There are five power states:
OFF
DEEP_SLEEP - the real-time clock runs but all other parts of the chip are closed
SLEEP - consumes less than 12uA with only real-time clock and watchdog running. The chip will wake on MAC, host, RTC or external interrupt.
WAKEUP - the system is changing from a sleep to on state. Crystal oscillator and PLL are enabled.
ON - consumes less than 1.0mW (DTIM = 3) or 0.5mW (DTIM = 10).
The Real-time clock can be programmed to wake the ESP8266 within a specified period of time.
The higher the DTIM period, the longer the device may sleep and therefore the more power the device may potentially save.
To meet the power requirements of mobile applications and wearable electronics, to reduce the overall power consumption, the PA output power can be customised in the firmware.
Application Ideas
Home automation
Sensor networks
Mesh networking
Wearable electronics
Baby monitor
Network camera
Industrial wireless control
WiFi beacons
Smart power plug
Location-aware applications
Getting Started
After this section, you can make Grove - UART WiFi run with only few steps.
Preparations
Now we are making a demo for wireless access point(AP) scan which require following modules.
If this is your first time using Seeeduino Lite, please refer to Seeeduino Lite's wiki
Seeeduino Lite is compatible with Arduino which works as simple as Arduino.
If this is your first time using Arduino, Please put hand on here to start your Arduino journey.
Connecting hardware
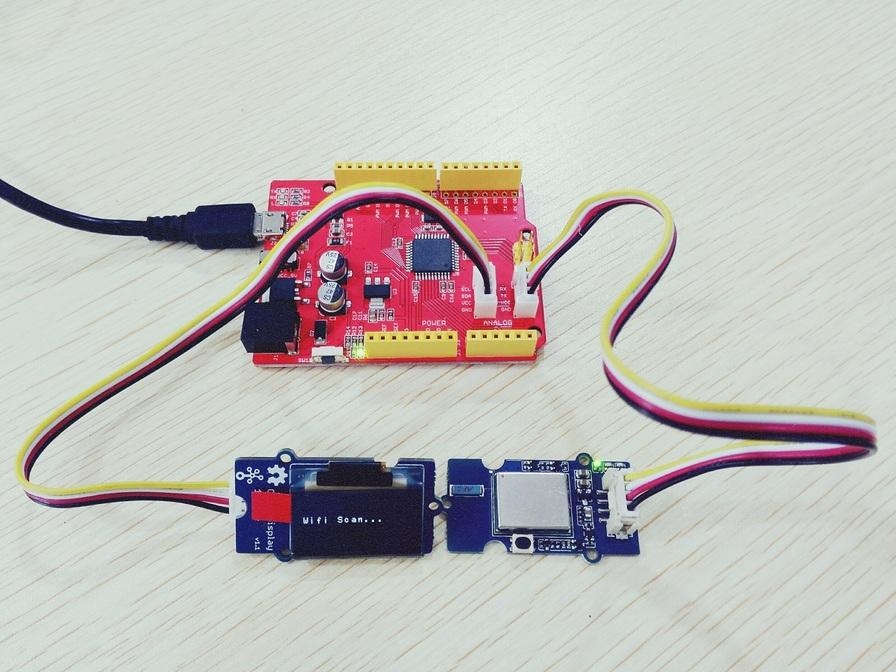
Seeeduino Lite got Grove socket for connecting two module mentioned above: Grove - OLED Display 1.12 and Grove - Uart Wi-Fi.
They are:
Grove - OLED Display 1.12 - connection to I2C socket
Grove - UART Wifi - connection to Serial socket
*
As shown below:
Download
Click here to download testing code and decompress it to any folders(e.g. Drive D or desktop)
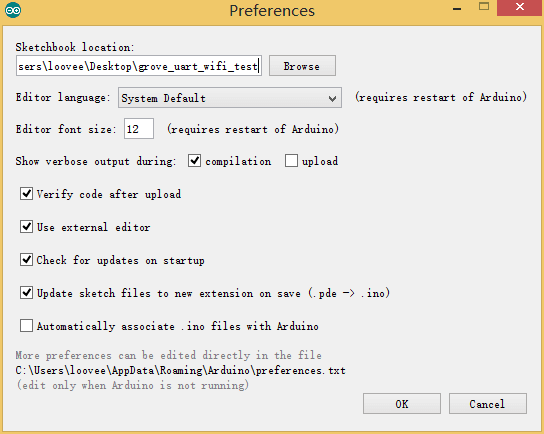
Now you need simple configurations for Arduino sketchbook.
Launch Arduino IDE and click File>Preferences and add absolute location for downloaded testing code at Sketchbook location .
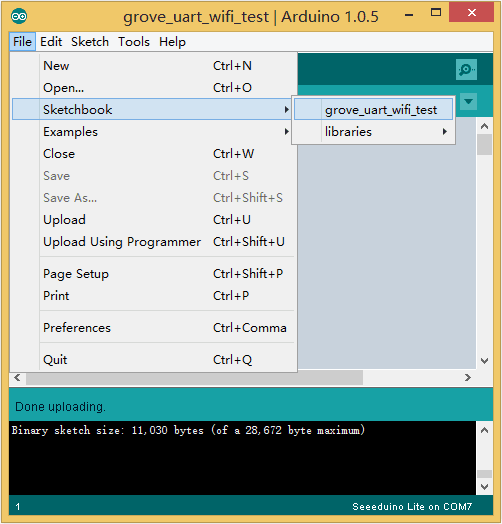
After configurations, please restart Arduino, click File>Sketchbook and choose grove_uart_wifi_wiki after which testing code will show up.
Click Tools>Board to choose Seeeduino Lite and select respective serial port.
Now click Upload(CTRL+U) to burn testing code. Please refer to here for any error prompt and you can also add comment on forum
Review Results
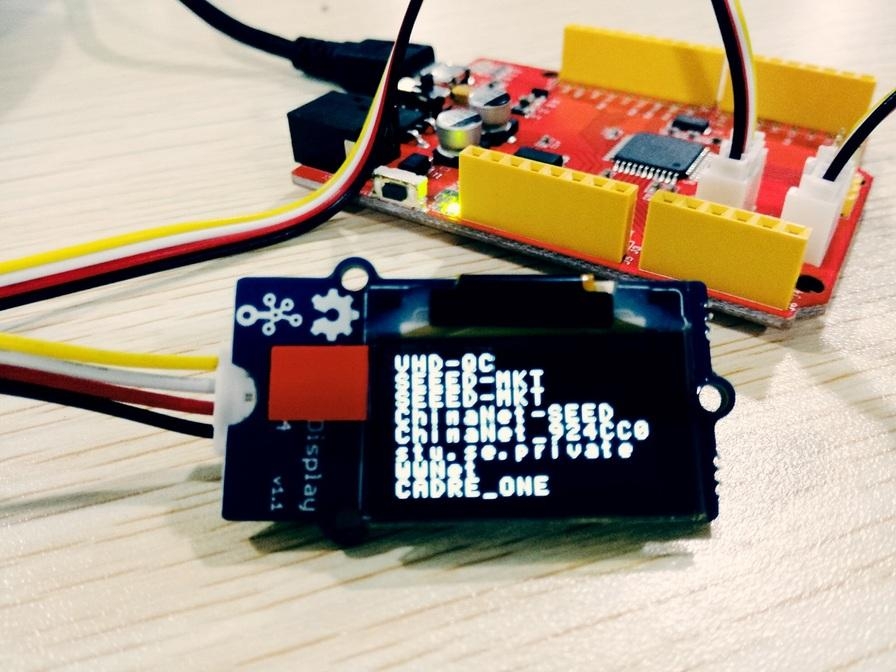
After upload completed, you can see AP identifier on OLED display.Following AP identifiers are found in our office.
Firmware update
Our module board got a firmware burned into it for factory settings, you can burn other firmware to it if you like. Click here to download source code of factory setting firmware.
Preparations
A USB to serial converter is required for firmware updating, you can choose UartSBee V5 we offered if you don't know where to get one.
A Grove-Jump converting cable is required and we also offered for sale. Click here to check.
A micro USB cable(type A to type C) is required.
Connecting hardware
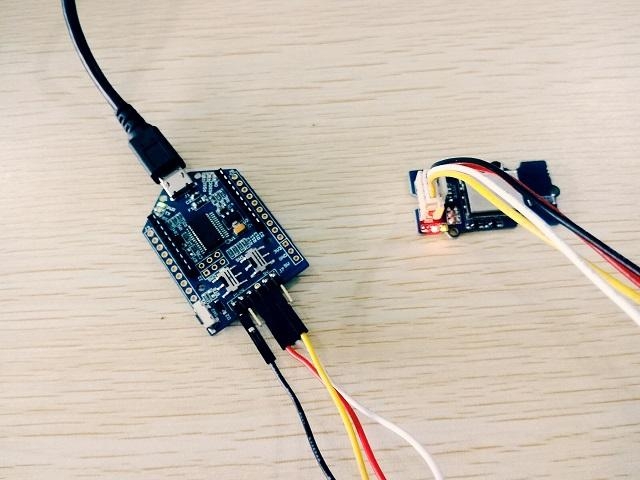
1.Connect one end of Grove-Jump converting cable with grove socket on Grove - Uart Wifi and connect other end with UartSBee V5 which shown as following.
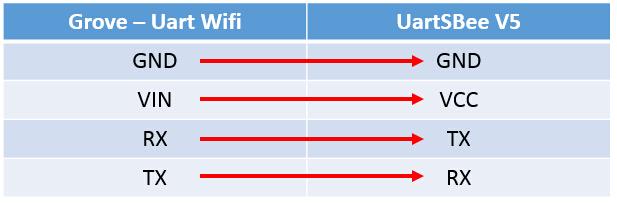
2.Then connecting cables like following figure:
Download burning tools
Operation steps
Now make sure you have downloaded burning software and bin file of firmware. Let us start burning to board.
Press and hold button until red LED indicator light on which indicate it is ready to burn firmware.
Start executable files in FLASH DOWNLOAD TOOLS files (double click) to make configurations like following steps:
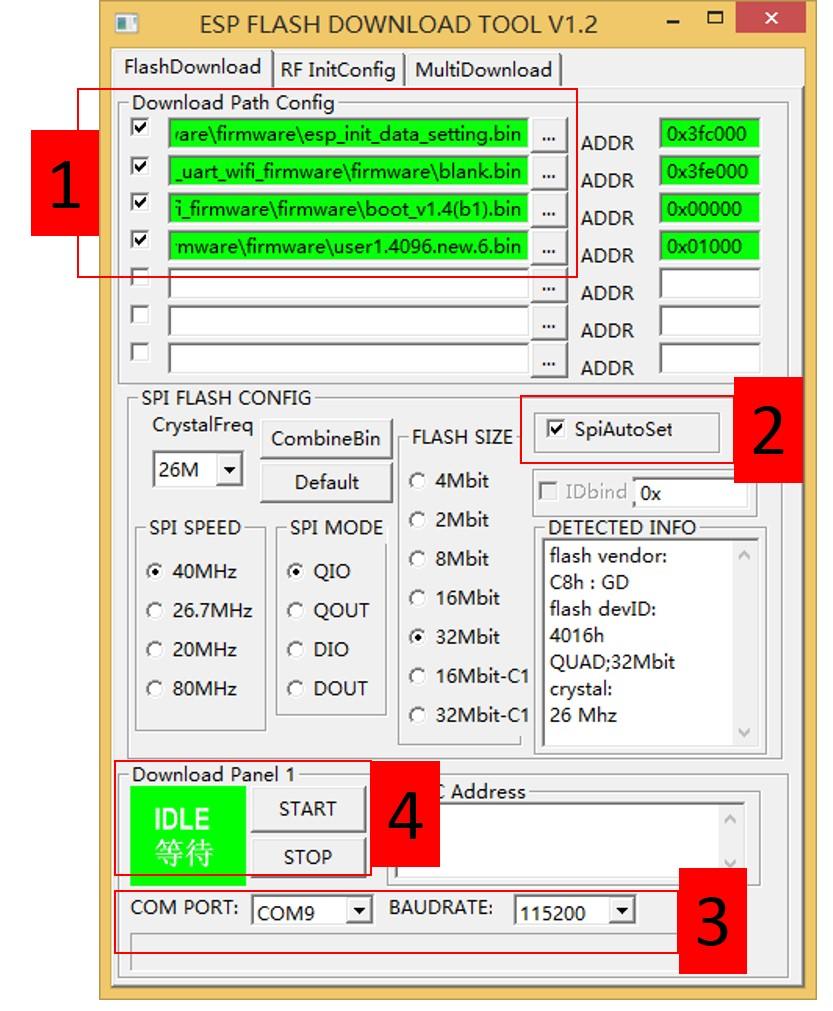
1. Choose desired files from firmware bin file downloaded.
2. Check SpiAutoSet.
3. Choose respective COM port and BAUDRATE.
Click to START to burn firmware
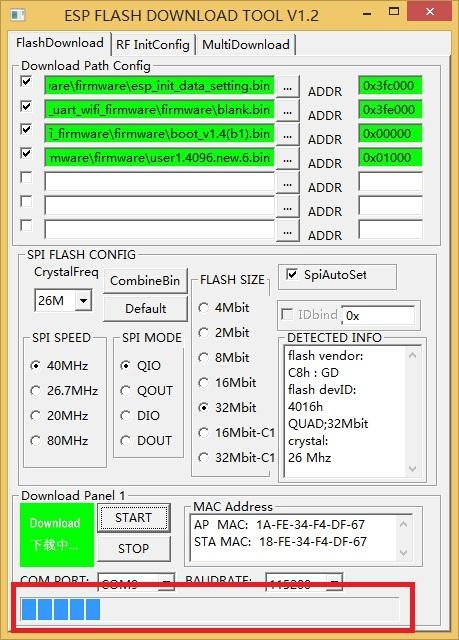
Progress bar will be displayed in firmware-burning process.
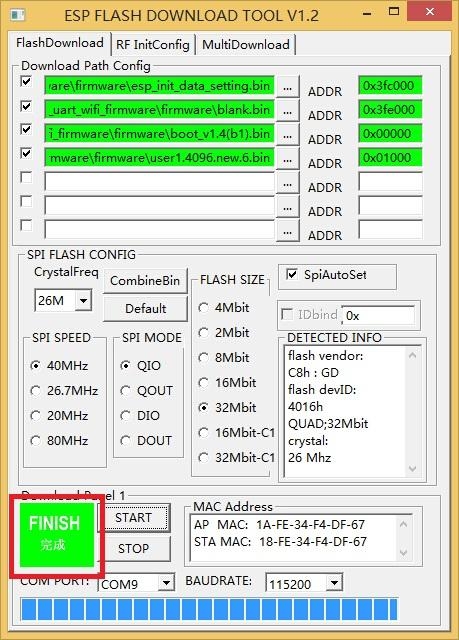
Finally, firmware-burning is done.
AT Commands
Using Espressif Systems ESP8266 AT Instruction Set Version 0.24 with SeeedStudio additions.
Basic AT Commands
Command
Description
AT
Test AT startup
AT+RST
Restart module
AT+GMR
View version info
AT+GSLP
Enter deep-sleep mode
ATE
Enable/Disable AT commands echo
AT+RESTORE
Factory Reset
AT+UART
UART configuration(Deprecated)
AT+UART_CUR
UART current configuration (Won't save to Flash)
AT+UART_DEF
UART default configuration (Save to Flash)
AT+SLEEP
Sleep mode
AT+RFPOWER
Set RF TX Power
AT+RFVDD
Set RF TX Power according to VDD33
WiFi AT Commands
Command
Description
AT+CWMODE
WIFI mode (Deprecated)
AT+CWMODE_CUR
Current WIFI mode (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CWMODE_DEF
Default WIFI mode (Save to Flash)
AT+CWJAP
Connect to AP (Deprecated)
AT+CWJAP_CUR
Current Connect to AP (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CWJAP_DEF
Default Connect to AP (Save to Flash)
AT+CWLAP
Lists available APs
AT+CWQAP
Disconnect from AP
AT+CWSAP
Configure softAP (Deprecated)
AT+CWSAP_CUR
Configure current softAP (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CWSAP_DEF
Configure default softAP (Save to Flash)
AT+CWLIF
List stations connected to softAP
AT+CWDHCP
Enable/Disable DHCP (Deprecated)
AT+CWDHCP_CUR
Current Enable/Disable DHCP (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CWDHCP_DEF
Default Enable/Disable DHCP (Save to Flash)
AT+CWAUTOCONN
Connect to AP automatically when power on
AT+CIPSTAMAC
Set station mac address (Deprecated)
AT+CIPSTAMAC_CUR
Set station mac address (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CIPSTAMAC_DEF
Set station mac address (Save to Flash)
AT+CIPAPMAC
Set softAP mac address (Deprecated)
AT+CIPAPMAC_CUR
Set softAP mac address (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CIPAPMAC_DEF
Set softAP mac address (Save to Flash)
AT+CIPSTA
Set station IP address (Deprecated)
AT+CIPSTA_CUR
Set station IP address (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CIPSTA_DEF
Set station IP address (Save to Flash)
AT+CIPAP
Set softAP IP address (Deprecated)
AT+CIPAP_CUR
Set softAP IP address (Won't save to Flash)
AT+CIPAP_DEF
Set softAP IP address (Save to Flash)
AT+CWSTARTSMART
Start SmartConfig
AT+CWSTOPSMART
Stop SmartConfig
TCP/IP AT Commands
Command
Description
AT+CIPSTATUS
Get connection status
AT+CIPSTART
Establish TCP connection or register UDP port
AT+CIPSEND
Send data
AT+CIPSENDEX
Send data, if or "\0" is met, data will be sent
AT+CIPSENDBUF
Write data into TCP-send-buffer
AT+CIPBUFRESET
Reset segment ID count
AT+CIPBUFSTATUS
Check status of TCP-send-buffer
AT+CIPCHECKSEQ
Check if a specific segment is sent or not
AT+CIPCLOSE
Close TCP/UDP connection
AT+CIFSR
Get local IP address
AT+CIPMUX
Set multiple connections mode
AT+CIPSERVER
Configure as server
AT+CIPMODE
Set transmission mode
AT+SAVETRANSLINK
Save transparent transmission link to Flash
AT+CIPSTO
Set timeout when ESP8266 runs as TCP server
AT+CIUPDATE
Upgrade firmware through network
AT+PING
Ping an IP address or hostname
Seeed AT Commands
Command
Description
AT+LEDON
Turn the blue LINK led on
AT+LEDOFF
Turn the blue LINK led off
Resources
Last updated