Grove Electricity Sensor
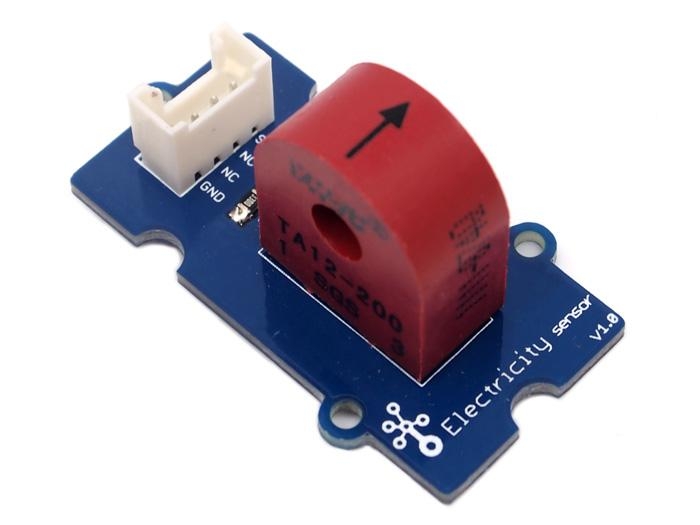
The Electricity sensor module is a member of Grove. It is based on the TA12-200 current transformer which can transform the large AC into small amplitude. You can use it to test large alternating current up to 5A.
Features
Grove compatible interface
Maximum 5A input
High accuracy
Small size
!!!Tip More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Application Ideas
Alternating current measurement
Device condition monitoring
Specification
Key Specification
Items
Min
PCB Size
2.0cm*4.0cm
Interface
2.0mm pitch pin header
IO Structure
SIG,NC,NC,GND
RoHS
YES
Electronic Characteristics
Items
Min
Norm
Max
Unit
Transformation ratio
-
2000:1
-
-
Input Current
0
-
5
A
Output Current
0
-
2.5
mA
Sampling Resistance
-
800
-
Ω
Sampling Voltage
0
-
2
V
Working Frequency
20
-
20K
HZ
Nonlinear scale
-
-
0.2%
-
Phase Shift
-
-
5'
-
Operating Temperature
-55
-
85
℃
Dielectric strength
-
6
-
KVAC/1min
Platforms Supported
Usage
With Arduino
The following sketch demonstrates a simple application of measuring the amplitude of the alternating voltage. The SIG pin will output a alternating voltage based on the alternating current being measured. You can measure the value using ADC.
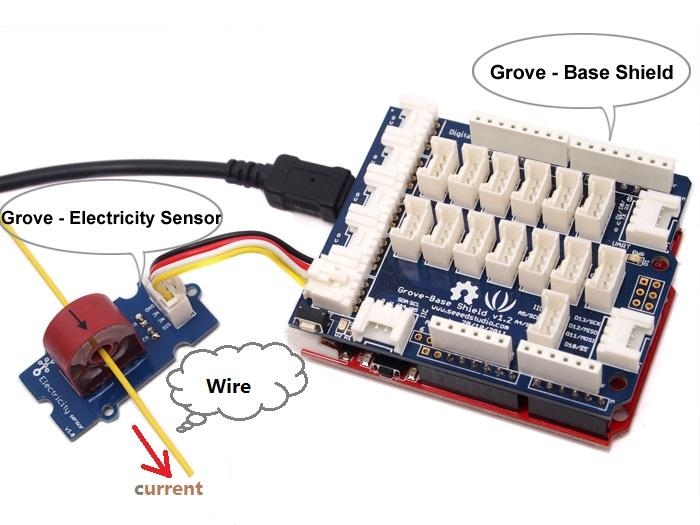
Connect the module to the analog A0 of Grove - Base board.
Put the alternating current wire through the hole of the current transformer.
Copy and paste code below to a new Arduino sketch.
Upload the code.
Note The minimum effective current that can be sensed by the code can be calculated using the equation below. minimum_current=1/1024*5/800*2000000/1.414=8.6(mA).
Open the serial monitor, The results is as follows:

With Raspberry Pi
1.You should have got a raspberry pi and a grovepi or grovepi+.
2.You should have completed configuring the development enviroment, otherwise follow here.
3.Connection
Plug the sensor to grovepi socket A0 by using a grove cable.
4.Navigate to the demos' directory:
To see the code
5.Run the demo.
Resources
Last updated