Grove 3 Axis Digital Accelerometer 16g
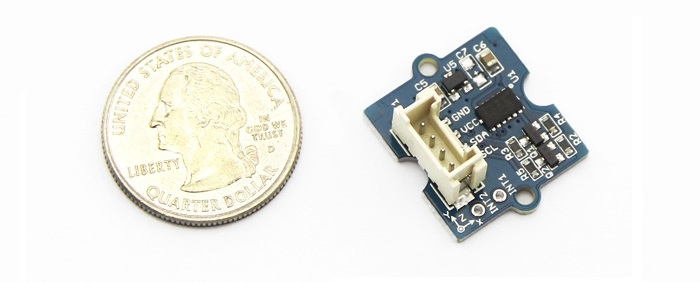
3-Axis Digital Accelerometer is the key part in projects like orientation detection, gesture detection and Motion detection. This 3-Axis Digital Accelerometer(±16g) is based on low power consumption IC ADXL345. It features up to 10,000g high shock survivability and configurable Samples per Second rate. For generous applications that don't require too large measurement range, this is a great choice because it's durable, energy saving and cost-efficient.
Specifications
Working voltage: 3.0 - 5.5V
Test Range: ±16
Sensitivity: 3.9mg / LSB
Standby Current: 0.1μA(Under stand mode Vcc = 2.5 V (typical))
10000 g high shock survivability
ECOPACK®RoHS and “Green” compliant
Suli-compatible Library
!!!Tip
More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Demonstration
With Arduino
Every accelerometer has been individually tested before shipping to you. But in rare cases, you might need to reset the zero-offset by yourself. Here below we show you how to read the raw data and obtain data in the unit of g, AKA g-force, from this accelerometer.
Step1: Plug it onto the I2C port of your Grove - Base Shield.
Step2: Download the Digital Accelerometer(±16g) Library .zip and unpack it into arduino-1.0\libraries in your Arduino installation folder. If you don't know how to install library for Arduino, please follow the toturial How to install an Arduino library
Step3: If you have the library installed, Open the demo code directly by the path:
File(文件) -> Example(示例) ->DigitalAccelerometer_ADXL345->ADXL345_demo_code.
Step4: Upload the code and open the serial monitor(usually it is on the right up corner). Please refer to the toturial Upload code if you do not know how to upload.
Step5: The result will be showed as the format in below image, shake the grove and you will find the number changing.
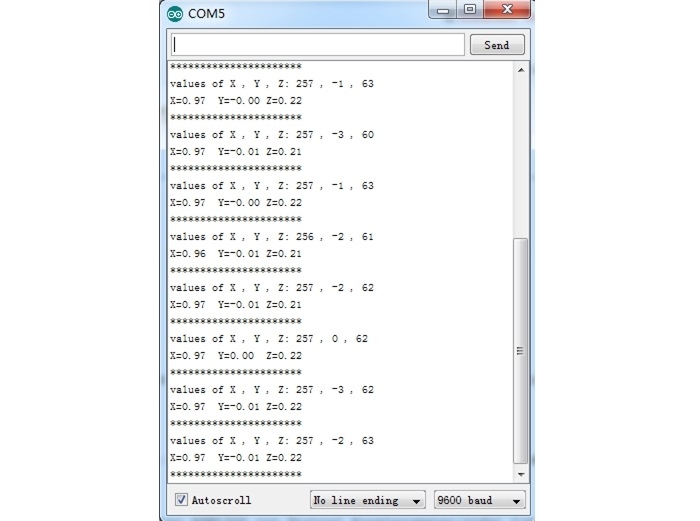
The outputs of this sensor consist of two parts: raw data and 3-axis acceleration info converted into the unit of gravity, "g".
With Raspberry Pi
Step1: You should have got a raspberry pi and a grovepi or grovepi+.
Step2: You should have completed configuring the development enviroment, otherwise follow here.
Step3: Connection
Plug the sensor to grovepi socket i2c-x(1~3) by using a grove cable.
Step4: Navigate to the demos' directory:
To see the code
5.Run the demo.
With Beaglebone Green
To begin editing programs that live on BBG, you can use the Cloud9 IDE. As a simple exercise to become familiar with Cloud9 IDE, creating a simple application to blink one of the 4 user programmable LEDs on the BeagleBone is a good start.
If this is your first time to use Cloud9 IDE, please follow this link.
Step1: Set the Grove - UART socket as a Grove - GPIO Socket, just follow this link.
Step2: Click the "+" in the top-right to create a new file.
Step3: Copy and paste the following code into the new tab.
Step4: Save the file by clicking the disk icon with with the .py extension..
Step5: Connect Grove - 3-Axis Digital Accelerometer(±16g) to Grove I2C socket on BBG.
Step6: Run the code. You'll sfind that the terminal outputs Gravity info every 2 seconds.
Resources
Last updated