Grove I2C Motor Driver V1.3
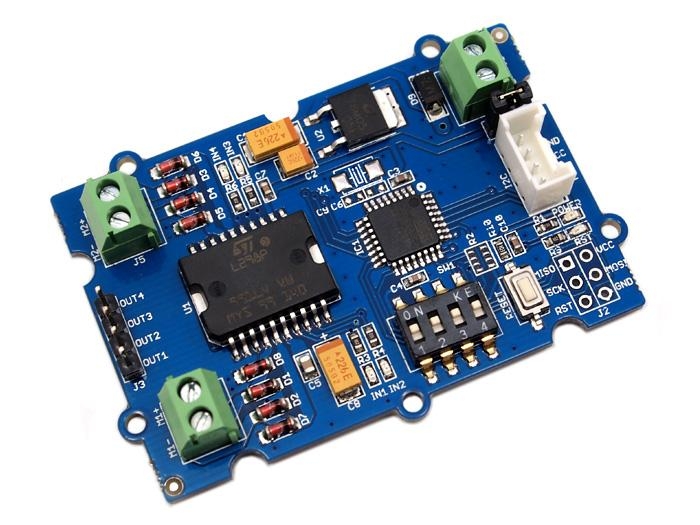
The Grove - I2C Motor Driver V1.3 (latest version) can directly control Stepper Motor or DC Motor. Its heart is a dual channel H-bridge driver chip(L298N)that can handle current up to 2A per channel, controlled by an Atmel ATmega8L which handles the I2C communication with platforms such as Arduino. Both motors can be driven simultaneously while set to a different speed and direction. It can power two brushed DC motors or one 4-wire two-phase stepper motor. It requires a 6V to 15V power supply to power the motor and has an onboard 5V voltage regulator which can power the I2C bus and the Arduino(selectable by jumper). All driver lines are protected by diodes from back-EMF.
Contrast to the Grove - I2C motor driver V1.2, the V1.3 enables users to control the stepper motor more easily. You do not need to control the steppers all the time anymore, simply send a command to I2C motor driver V1.3 to drive a stepper motor, and it will act as your command, which would save your Arduino resource and simplify your code.
Version
Revision
Descriptions
Release
v1.0
Initial public release
May 17th, 2012
v1.2
Modify the I2C address set by hardware
July 2nd, 2012
v1.3
Modify the firmware to support off-line Stepper
Feb 18th, 2013
Features
Grove Compatible
I2C Interface
Adjustable motor speed and rotation direction
Changeable slave address by hardware
!!!Tip More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Specifications
Item
Min
Typical
Max
Unit
Working Voltage
6
-
15
VDC
Max Output Current per channel
0.5
A
Maximum Total current
1.0
A
Input/output voltage on I2C bus
5
V
Communication protocol
I2C
/
Platforms Supported
Hardware Overview
 78M05 IC: 5V voltage regulator
78M05 IC: 5V voltage regulator
L298 IC: Dual full bridge driver
ATmega8 IC: Control Motor Rotation.
Note Input voltage on screw terminals is regulated to 5V and connected to I2C +5V via a jumper (J4). Remove jumper if both external power via the screw terminals and power via the I2C header are used. Use jumper if 5V should be supplied to the I2C bus.
Application Ideas
Robots
Homebuilt RC cars
Case fans
High power LED illumination
Caution The board will be very hot while operating over 1Amp. Do keep your hands off!
Getting Started
The I2C Motor Driver can control motor which is based on the chip L298. The L298 isn’t just a dual motor driver, it is a dual H-bridge. An h-bridge is basically a specific setup of transistors that allow you to switch direction of current. Hooking up to a motor means you can have it spin in both directions; and with PWM input, you can use your Arduino to make them spin at any speed. Because the L298 has 2 H-bridges, you can make a robot turn around by spinning each wheel in different directions, and of course go forwards and backwards.
1. Install the library
Please follow how to install an arduino library procedures to install library.
Run the command or or download the zip file directly.
Simply copy the Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3 folder to your Arduino library collection. For example, arduino-1.6.12/libraries. Next time you run the Arduino IDE, you'll have a new option in Sketch -> Include Library -> Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3. Review the included examples in Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3. We provide both DC and stepper motor control examples.

2. Set the address of the I2C Motor Driver
Set the address by dial switch is a new function added to the new I2C Motor Driver.

Then keep the address setup in the program the same as the address setup on the I2C motor driver. The default address setup in the program is 0x0f.
3. Drive 2 DC motors
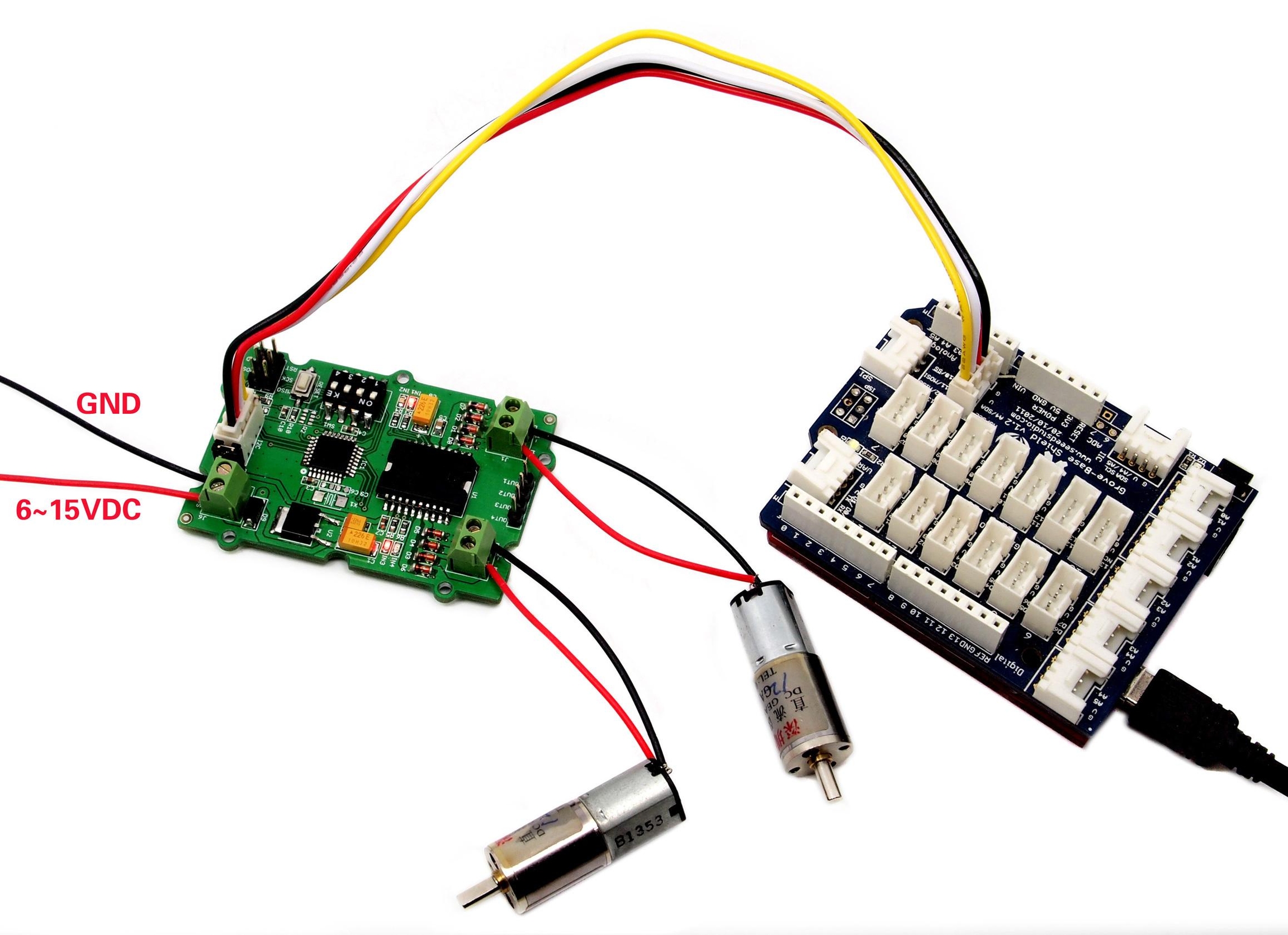
Note The first thing to notice, is that you need an external power source for your DC motors. The 5V pin on the Arduino cannot provide enough power to drive 2 motors, you may damage your Arduino if you do so.
There are 2 functions to control DC motors:
With speed() function, you are able to drive one motor at the speed you want.
motor_id represents which motor to use. You can fill MOTOR1 or MOTOR2.
_speed represents the speed you set to the motor. You can fill -100~100 here. When _speed>0, DC motor runs clockwise, while _speed<0, DC motor runs anticlockwise. And the bigger the absolute value of _speed, the faster the speed of DC motor.
With stop() function, you are able to stop a running DC motor.
motor_id represents which motor to use. You can fill MOTOR1 or MOTOR2.
4. Drive a Stepper Motor
Take 24BYJ48 Stepper Motor as an example, The hardware installation as shown below:
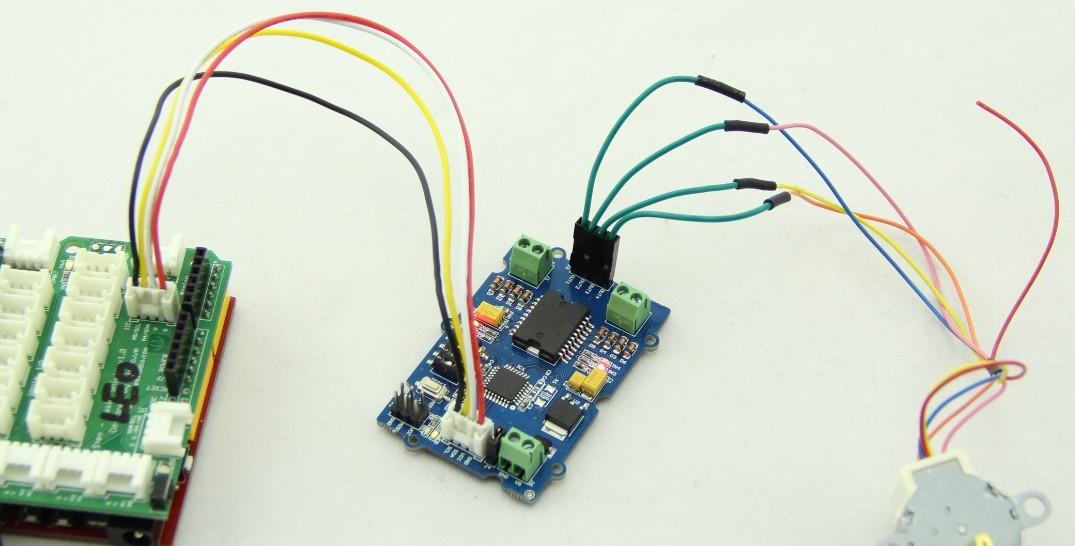
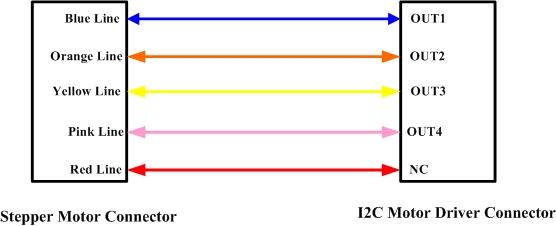
The connection between 24BYJ48 Stepper Motor and I2C Motor Driver is as shown below:
We provide one function to drive a stepper motor.
_step represents the steps you set to the stepper motor to run. You can fill -1024~1024. When _step>0, stepper motor runs clockwise, while _step<0, stepper motor runs anticlockwise. When _step is 512/-512, the stepper motor will run a complete turn and if _step is 1024/-1024, the stepper motor will run 2 turns. The stepper motor will stop automatically after it finishes its steps.
Resources
Last updated
Was this helpful?